From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| |||||||||||||||||||
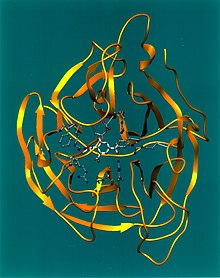
Viral neuraminidase is an enzyme on the surface of influenza viruses that enables the virus to be released from the host cell. Drugs that inhibit neuraminidase are used to treat influenza.
When influenza virus reproduces, it moves to the cell surface with a hemagglutinin molecule on the surface of the virus bound to a sialic acid receptor on the surface of the cell. In order for the virus to be released free from the cell, neuraminidase must break apart (cleave) the sialic acid receptor. [2]
In some viruses, a hemagglutinin-neuraminidase protein combines the neuraminidase and hemagglutinin functions in a single protein.





No comments:
Post a Comment